Internal Space Zones for Energy Evaluation
Create a zone in every conditioned space of the building, using exclusively the Inner Edge zone construction method. Energy Evaluation is not compatible with zones created with the Manual construction method. The zones must be directly adjacent to the surrounding elements’ surfaces, therefore the Reference Line zone construction method is not applicable for energy modeling either.

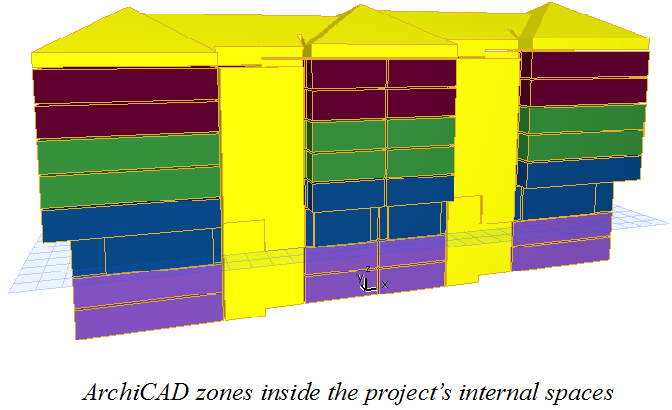
3D Zone Boundaries
When placing zones on the floor plan, make sure that they are completely enclosed by zone boundaries.
•All ARCHICAD walls (including profiled curtain walls) automatically behave as zone boundaries.
•When using Slabs as bottom or top zone boundaries, make sure that the zone level and/or height are set so that the horizontal zone surface(s) touch the inner edge of the Slab(s).
•If Roofs, Meshes, Shells, Morphs or ARCHICAD library objects are used as zone boundaries, an additional interaction is required besides just creating the zone. In such situations:
◦Draw the zone manually, making sure that it extends beyond the Roof, Mesh, Shell zone boundary elements completely.
◦Use a command from the Design > Connect menu, such as Trim Elements or Solid Element Operations, to shape the zone with the selected zone boundaries and establish the connection between them.
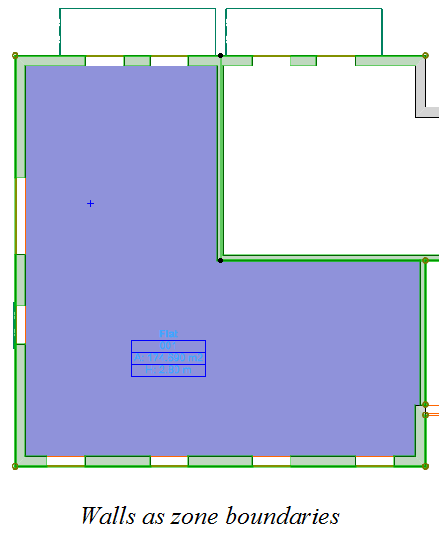
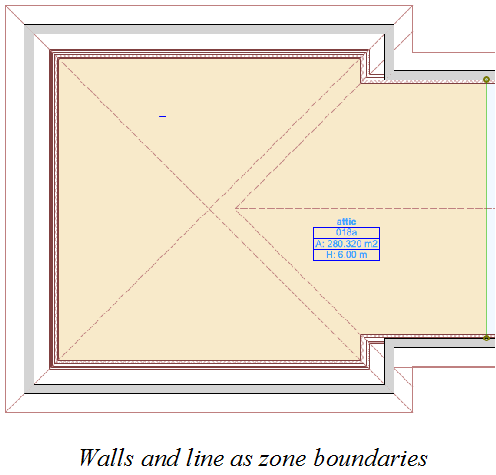
2D Zone Boundaries
It is also possible to define lines on the floor plan as 2D zone boundaries. Select the line(s) you want to behave as zone boundaries and tick the Zone Boundary checkbox on the Line Selection Settings dialog.
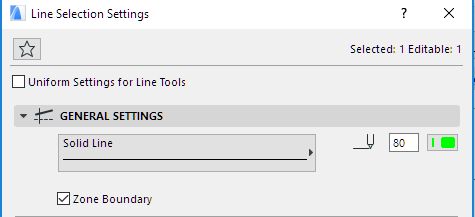
There are a number of modeling scenarios that make it necessary to define lines as Zone Boundaries. For example:
•Modeling perimeter zones in Core and Shell projects
•Atria in buildings
•Spaces that contain several, dramatically different floor and/or roof levels

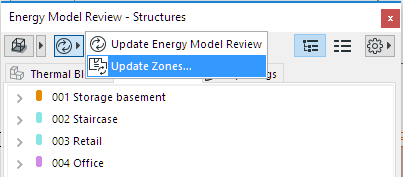
Update Zones
Use the Update Zones command on the left upper corner of the Energy Model Review palette after altering the geometry of zones or zone boundaries. This will ensure that the energy model reflects the up-to-date state of the ARCHICAD model.
Zone Modeling Conventions
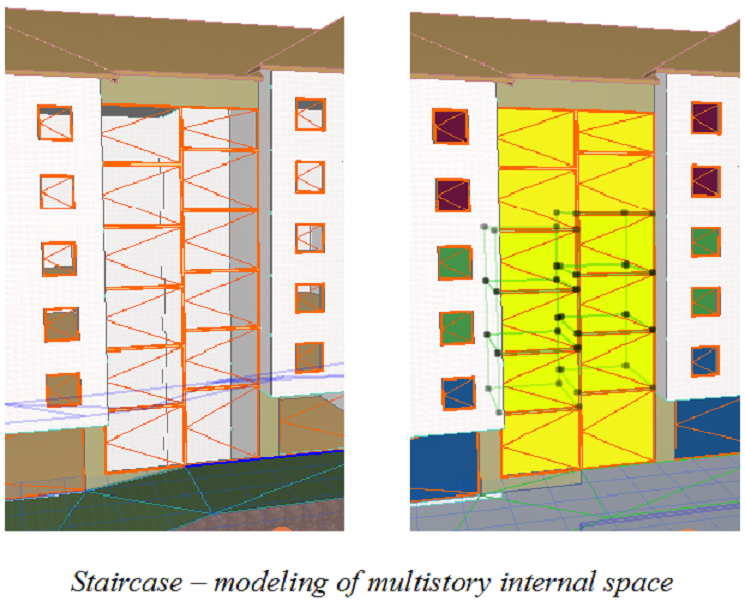
•Model multistory internal spaces (e.g. staircase blocks, atria) with separate zones on every ARCHICAD Story.
•Adiabatic walls are walls of the building shell that separate heated spaces. They are called adiabatic due to the absence of heat transfer through them. A typical example is a fire wall separating row-houses or other adjacent buildings.
In such situations, model the surfaces of the neighboring building that are adjacent to your building, with thin ARCHICAD zones. Use a separate zone on every story of your project.