Building Material properties for environmental sustainability (Selected markets)
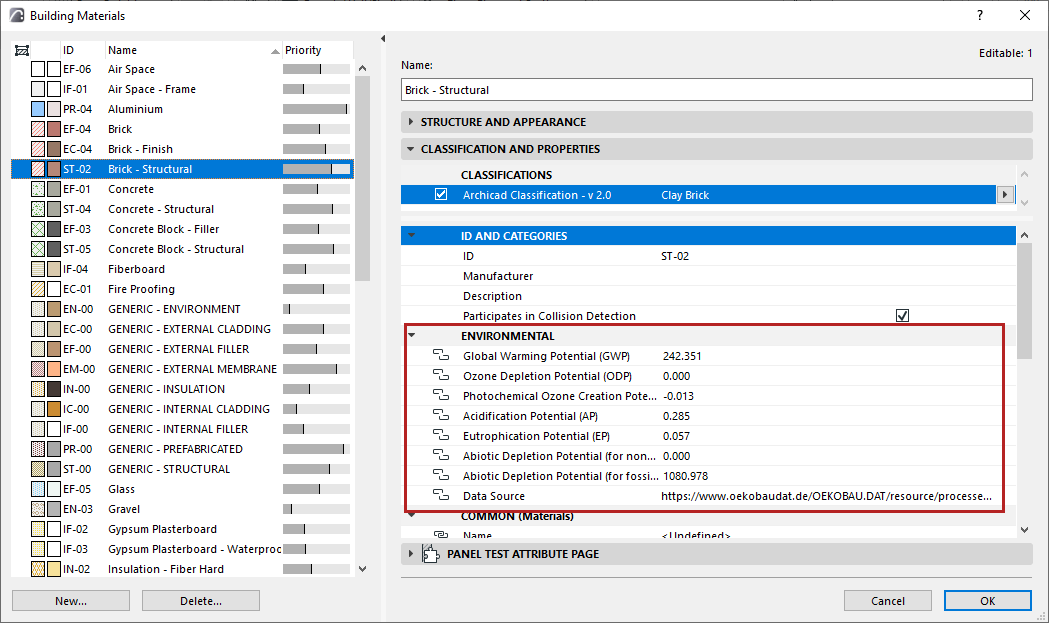
Archicad 26 includes a new set of Building Material properties, corresponding to standard environmental indicators.
Note: These new properties are available out-of-the-box for the INT template, plus in language versions based on the INT template.
Property values are based on data of the German ÖKOBAUDAT database. Use these validated properties to document embedded energy and CO2 footprint data for building lifecycle analysis and sustainability reports.

New Archicad properties in the ENVIRONMENTAL property group
These correspond to the EN 15804 sustainability standard, whose indicators are required in EPDs (Environmental Product Declarations) for construction products.
|
Name |
Description |
|
Global Warming Potential (GWP) |
Global Warming Potential: the insulating effect of greenhouse gases (GHG) - CO2 and methane - in the atmosphere preventing the earth losing heat gained from the sun. As global temperature rises, it is expected to cause climatic disturbance, desertification, rising sea levels and spread of disease. Unit: kg CO2 eq. |
|
Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) |
Ozone Depletion Potential: depletion of the ozone layer (O3) in the atmosphere caused by the emission of chemical foaming and cleaning agents allows the passage of greater levels of UV from the sun, causing skin cancer, damage to the immune system and reducing crop yields. Unit: kg R11 eq. |
|
Photochemical Ozone Creation Potential (POCP) |
Photochemical Ozone Creation Potential: Creation of ozone in the presence of sunlight, nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds. Ozone leads to chemical smog that affect human health, food crops and the ecosystem in general. The effects vary according to geography and climate and are especially problematic in heavily urbanized areas with existing pollution. Unit: kg Ethene eq. |
|
Acidification Potential (AP) |
Acidification Potential: emissions, such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides from manufacturing processes, result in acid rain which harms soil, water supplies, human and animal organisms, and the ecosystem. Unit: kg SO2 eq. |
|
Eutrophication Potential (EP) |
Eutrophication Potential: increased concentrations of nitrates and phosphates can encourage excessive growth of algae and reduce oxygen levels. This increases mortality in aquatic fauna and flora, leads to loss of species dependent on low-nutrient environments, reduces biodiversity and has knock-on effects on non-aquatic animals and humans. Unit: kg Phosphate eq. |
|
Abiotic Depletion Potential (for non-fossil resources) (ADPE) |
Abiotic Depletion Potential for non-fossil resources: the over-extraction of minerals and other non-living, non-renewable materials which can lead to exhaustion of natural resources. Unit: kg Sb eq. |
|
Abiotic Depletion Potential (for fossil resources) (ADPF) |
Abiotic Depletion Potential for fossil resources: The over-extraction of fossil fuels including all fossil resources. Unit: MJ |
|
Data source |
Building life cycle assessment data sheet in the ÖKOBAUDAT database |