
To draw an arc or a full circle, choose the Arc/Circle tool in the Toolbox and one of the Geometry Methods offered by the first icon in the Info Box (Centerpoint, Three Points or Tangent Point).

Note: These methods are identical for drawing curved walls.
These methods use different basic points to define the arc.
•Centerpoint and radius
–Click to define centerpoint.
–Move the cursor to define the radius, then click a second time.
–Move the cursor to draw the length of the arc, then click to complete.
Note: To draw a full circle, double-click when defining its radius.

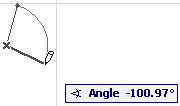
•Circumference
–Click on three points of the arc’s circumference (e.g. other elements or intersections, or special snap points).
–Click a fourth time to define the length of the arc.
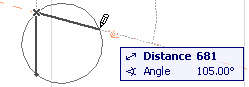
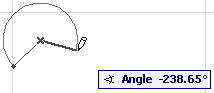
•Tangential: Define a full circle based on three tangential edges or points.
–Select three initial points: these can be a tangent edge, a node, or a free-floating point.
The next step depends on the geometric situation.
-If there is only one solution, the circle is automatically drawn.
-If there are multiple solutions, the Eyeball cursor appears and the ghost contour of the arc flips from one position to the other as you move the cursor around. Click when it is at the right place to complete the circle.
-If there is no solution, (for example, if you define three parallel edges for tangency), no circle will be made.
Note: Unlike circular Walls, Circles can be fully closed. You will obtain a single element, not two half-circles.