Linear Dimensions measure linear distances along an element, either straight or curved. Four construction methods are available in both the Info Box and Linear Dimension Tool Settings.
See Linear Dimension Tool Settings.
•With the Linear method, distances between two adjacent Reference Points are measured and displayed.
•With the Cumulative method, the first Reference Point is considered the zero point of the dimension chain. All dimension values of the chain will give you the distance between any Reference Point and the zero point.

•With the Base-line method, measuring the dimensioning distances is the same as with the Cumulative method, but the zero point is not marked.

•With the fourth icon, you create Elevation Dimensions.

For more information, see Elevation Dimensions.
Geometry Methods for Linear Dimensions are set in the Info Box.
•The default Any Direction method enables you to create dimension chains at a variety of positions relative to the element’s position: either parallel to the first two reference points placed, or horizontal/vertical, or parallel to another edge/surface of your choice.

•The X-Y Only method restricts the dimension line zones to horizontal and vertical only, relative to the screen.

•The Arc Length method allows you to dimension curved elements.

The Geometry Method you choose applies to the entire dimension chain, and cannot be set unit by unit.
Note: There are additional Geometry Methods for use in the 3D Document window.
See Linear Dimensions in the 3D Document Window.
Linear Dimension Line Placement Options
To dimension a straight element, place a series of dimension points along the element, then double-click.
The next step is to move the hammer cursor to the position where you want to place the dimension line.
When dimensioning a straight vertical or horizontal edge, a rubber band line provides feedback when placing the dimension line:
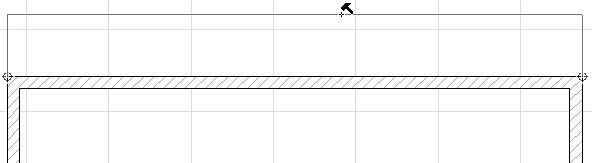
However, dimensioning an element in any other position - and if you are using the default Any Direction geometry method - will give you three dimension line options (“zones”): vertical, horizontal, or parallel to the first two dimension points in the chain. Move the cursor around to get feedback on the possibilities.
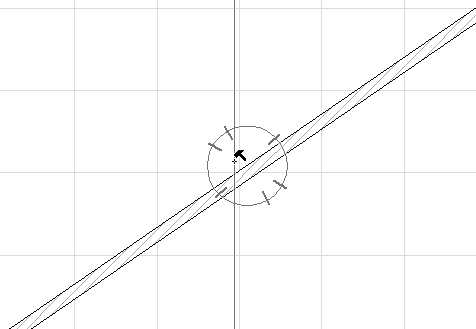
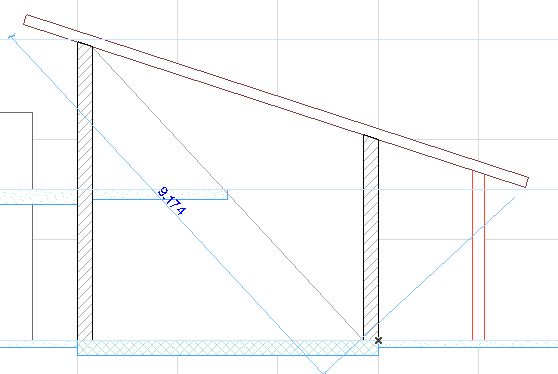
For example, when dimensioning the slanted roof in the Section below with the Any Direction method, use the parallel option to place the dimension line parallel to the roof:
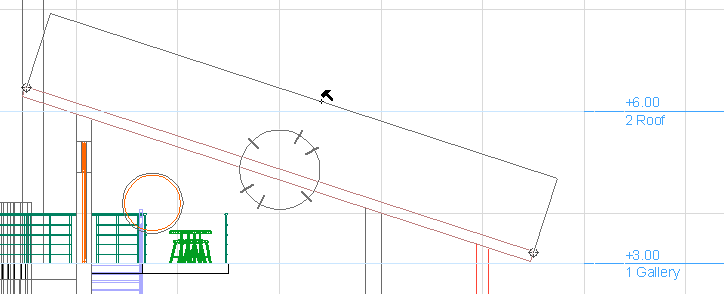
Alternatively, by moving the hammer cursor to another “zone”, you can choose a horizontal or vertical dimension instead:
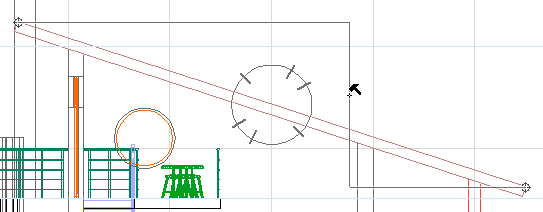
An additional dimension line vector is also available: After the black hammer cursor appears, you can move this cursor to any straight line/edge in the project.
Note: In the 3D Document window, you must align the dimension to the edge of a construction element - line segments do not work.
In the following image, we have dimensioned the slanted roof and the black hammer cursor appears, and the standard three dimension line directions (horizontal, vertical, parallel to roof) are available.
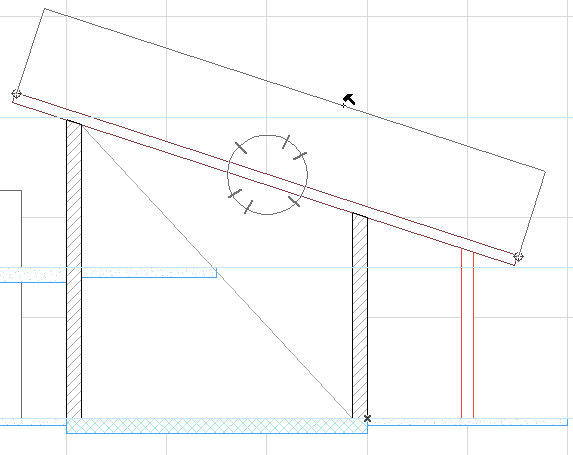
Suppose you want to dimension the roof using the vector parallel to the diagonal, instead of parallel to the roof. After clicking the two dimension nodes on either end of the roof, move the cursor over the diagonal. The cursor then changes to the “Mercedes + parallel dimension” cursor shape, to indicate that it has found an edge, to which the dimension line can be parallel:
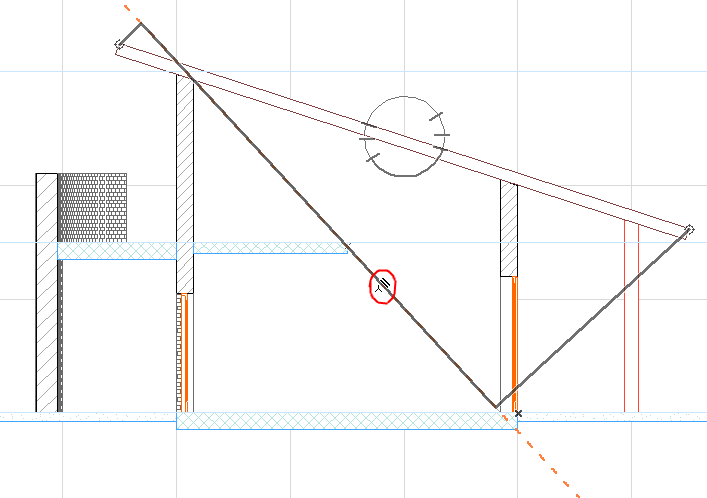
Click now to constrain the dimension line to be parallel to this line/edge.
Now drag the dimension line to its final position and click with the black hammer to place the dimension chain.
Linear Dimensioning of Curved Elements
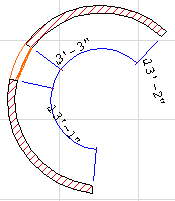
The Arc Length geometry method measures the length of a curved line or wall.
With the Linear Dimension tool active, choose the Arc Length Geometry Method from the Info Box.
•Click with the Mercedes cursor on a circular arc or a curved edge - you don’t have to find the end points, you can click anywhere on the curve.
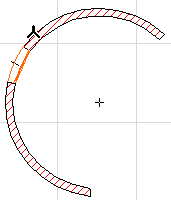
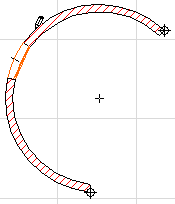
•ArchiCAD automatically marks the end points of the arc or the edge. This is the edge that arc length will be measured on. You may click any other points you want to add to the dimension chain.
•Double-click anywhere in the workspace with the Empty Pencil cursor or click the OK button in the Control Box to finish selecting arc points for dimensioning.
•The Hammer cursor appears, prompting you to place the dimension chain. Click to place the dimension chain.