Sampling (CineRender Global Illumination)
This setting is available, as part of the optional Global Illumination effect, in the Detailed view of PhotoRendering Settings for the CineRender engine.
The Sampling settings here only affect the GI sampling: How many samples should be sent and where in order to gather light from the environment? Samples are sent out hemispherically from the shading point (also called the “primary sampler”).
The Sampling settings affect the GI sampling for the QMC and IR Primary Method (if these are also used for the Secondary Method, only a fraction of the value defined here will be used):
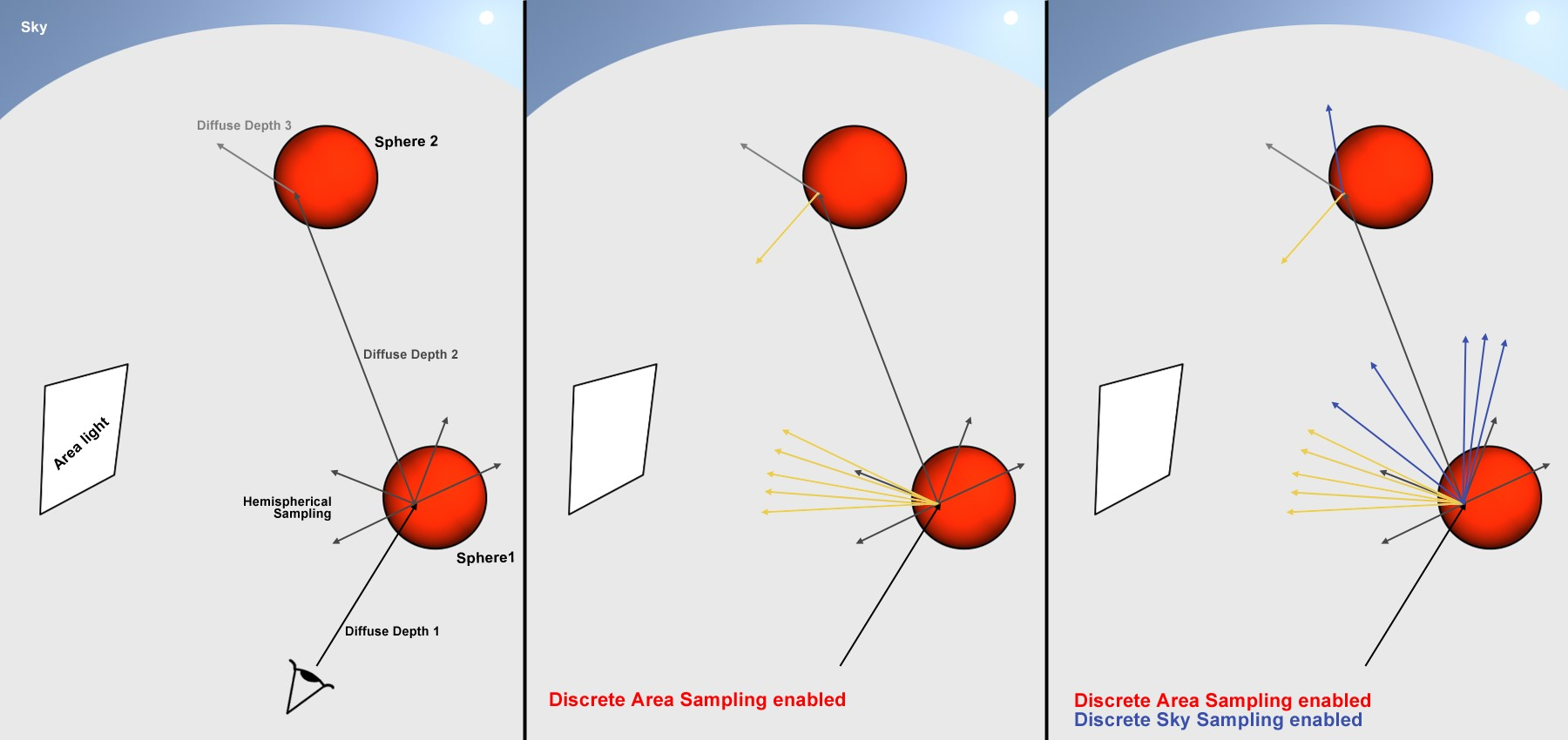
The image below shows how the QMC GI Mode works.

In the image above:
•Left (Discrete Area Sampling and Discrete Sky Sampling disabled): At the first point of contact, several samples are sent out in a hemispherical direction (this is exactly what the Hemispherical Sampling option is meant for).
•Center (Discrete Area Sampling is enabled and Discrete Sky Sampling is disabled): In addition to the hemispherical sampling, several samples are also sent out in the direction of Portals and (polygonal) lights.
•Right (Discrete Area Sampling and Discrete Sky Sampling enabled): In addition to the hemispherical sampling and the Area light sampling, additional samples are sent out in the direction of the sky.
The Sampling settings described below primarily define if and how many samples are created on Sphere 1.
In the following image, an Area light was positioned at the rear of the room. A window in the right-side wall looks out to a Sky object with an HDRI assigned to it (it can render hard shadows!). No other light sources have been placed in the project. The images were rendered with the QMC Primary Method (with the IC Method, you would see spots instead of graininess in the image).
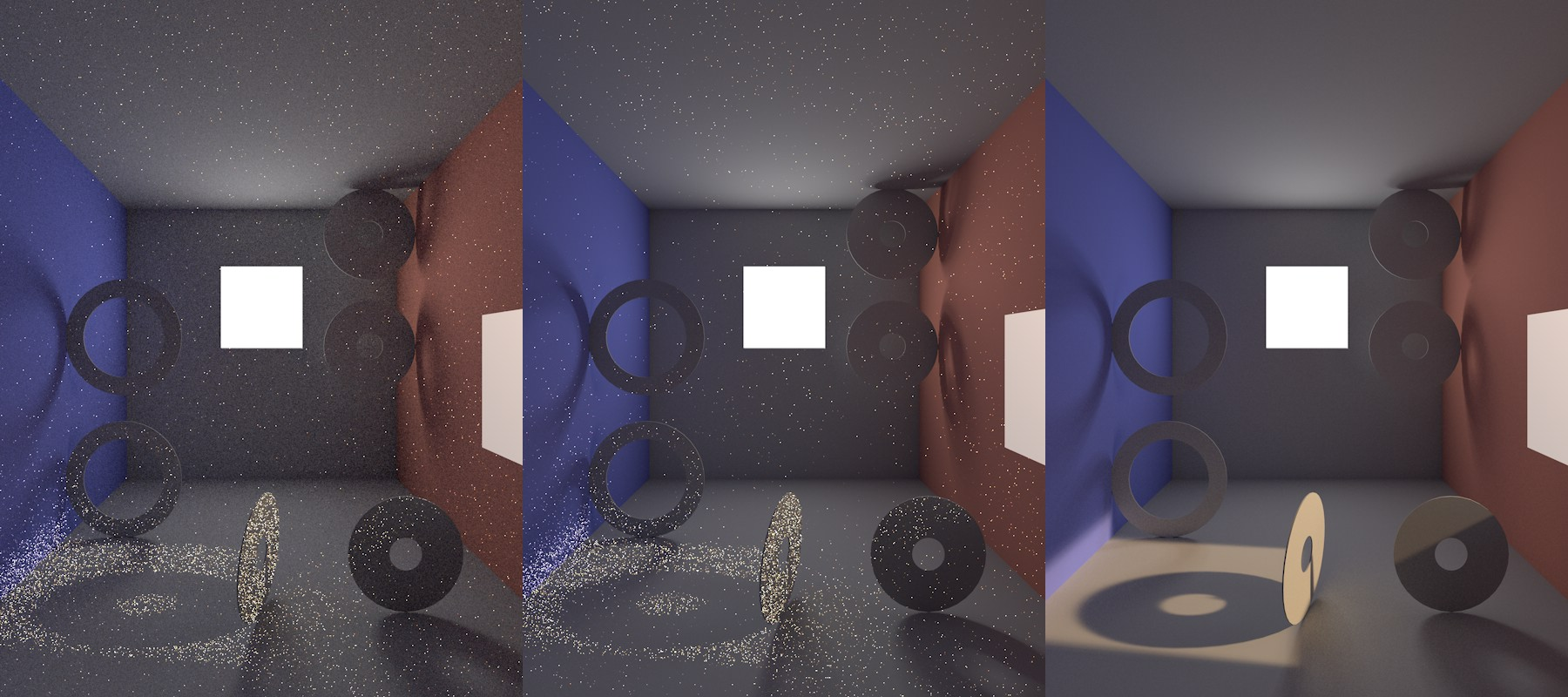
•Left (Discrete Area Sampling and Discrete Sky Sampling disabled): This is not a viable option for this particular Project. The image itself is very grainy (the result of random samples hitting the Area light). The shadows are even more grainy. Bright points are also visible, the result of very few random samples hitting the (HDRI) sky’s sun.
•Center (Discrete Area Sampling enabled and Discrete Sky Sampling disabled): The general graininess has been greatly reduced because additional samples are being sent to the Area light (each point visible to the camera is analyzed, which results in a highly defined shadow for the Area).
•Right (Discrete Area Sampling and Discrete Sky Sampling enabled): In addition to the hemispherical sampling and the Area light samples, additional samples are sent in the direction of the sky. This abolishes the bright points, because every point visible to the camera is precisely analyzed with regard to the sky’s influence (including its effect on the remaining project elements).
In general, you can leave Discrete Sampling enabled. Disable it only for special instances, to intentionally exclude one of the Sampling modes. The difference in render time will be noticeable if no Area light or sky is present in the project.
The description of the following settings applies to the QMC Primary Method. The same applies to the IR method, except that sampling takes places for each shading point, rather than for each pixel.
Stochastic Samples
Method: Two methods of defining sample count are used:
•An automatic determination controlled by one of the quality settings (Low, Medium, High, Accuracy)
•A fixed number of samples defined by the Sample Count setting

–Selecting Custom Sample Count lets you manually define the Sample Count value
–Selecting Custom Accuracy lets you manually define the Accuracy value
Accuracy: Use this setting to define an optimized sample count. The optimal count depends on the Project (and in IR GI Mode, on the other Irradiance Cache settings as well) and of course the defined Accuracy value.
Sample Count: This setting defines the fixed number of samples to be used. A higher value produces a correspondingly better render quality (for QMC this can be seen in the graininess; for IR the number of spots is reduced).

Increasing Sample Count (left to right)
This rendering Sample Count will also be used by the Discrete Area and Discrete Sky Sampling if they do not have a custom count defined (see below).
Discrete Area Sampling
Check Use Area Sampling to enable this method.
In order for this sampling type to work, the GI Area Light option must be enabled in the Surface’s Illumination channel.
See Illumination (CineRender Surface Channel).
This sampling method sends additional samples to (polygon) Area lights. This will emphasize them disproportionately, which will have a major effect on the quality of the GI.
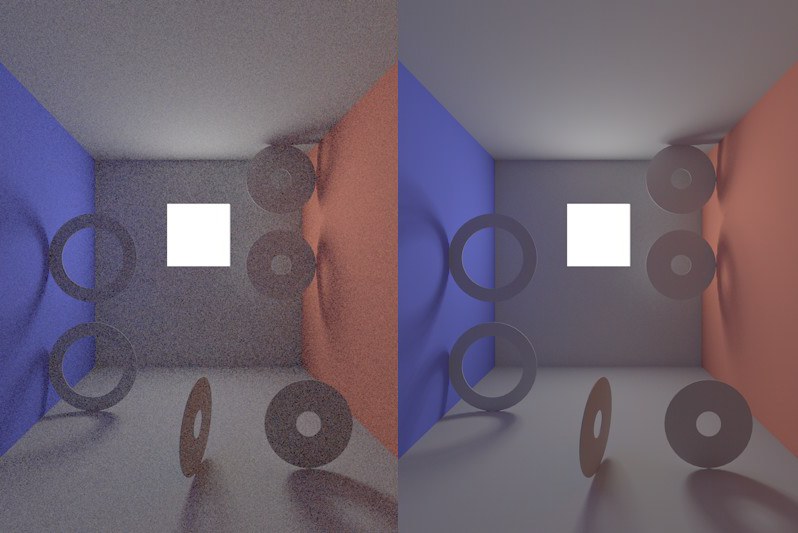
At center: Discrete Area Sampling disabled, at right: enabled
Note that even if you disable this option, the Area lights will NOT be omitted from the GI calculation. These lights will merely receive no special attention and will be hit randomly by the hemispheric sampling (with a correspondingly grainy result).
Force Per-Pixel: This option is only advantageous in IR Primary Method. Normally every light will be taken into consideration for the cache when an Irradiance Cache is created. However, this does not work if you have very small, bright Area lights. The result will be spotty images. If you enable the Force Per-Pixel option, the calculation of the Area lights will be split from the cache and calculated separately (as the QMC method does by default) for each potential pixel (object surfaces but no backgrounds or skies, for example).
![]()
At left, Force Per-Pixel disabled, at right: enabled
Custom Count/Sample Count
Use these fields to define a custom sample count. If Custom Count is disabled, the same number of samples will be used as defined in Stochastic Sampling.
Discrete Sky Sampling
Check Use Sky Sampling to enable this method.
This sampling mode takes into account the sky in particular (e.g., the Physical Sky or a HDRI Sky).
A sky map will be calculated internally during rendering, which will then concentrate the additionally created samples primarily on the brightest regions during rendering. This means that HDRI textures with enough contrast can cast shadows with locally very bright regions.
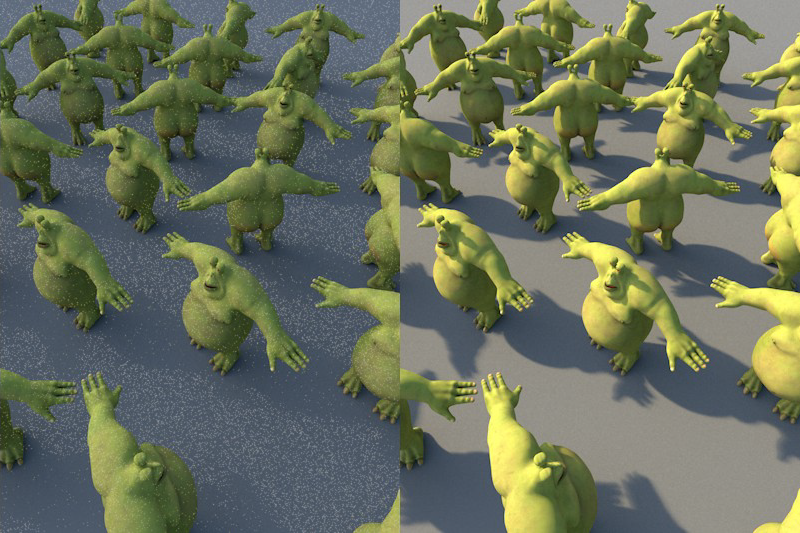
The only source of illumination here is the HDRI texture on a Sky object.
Note the relatively hard shadow (option disabled at left).
If this option is disabled, the sky will NOT be omitted from the GI calculation. The sky will merely receive no special attention and will be hit randomly by the hemispherical sampling (the extremely bright sun will produce a grainy image).
Force Per-Pixel: This option has advantages only for the IR Primary Method. When an Irradiance Cache is created, the sky will normally be sampled and taken into consideration for the cache. For bright regions (sun) or those with smaller surfaces, this method has limits and will result in spotty renderings.
If you enable Force Per-Pixel, the calculation of the light emitted by the sky will be split from the cache and calculated separately for each pixel that comes into question (object surfaces but no backgrounds, skies, etc.), which is how the QMC method works by default.
![]()
A Sky object with an HDRI texture applied to it is located behind the window.
At left, Force Per-Pixel disabled, at right enabled.
Custom Count/Sample Count
Use these fields to define a custom sample count. If Custom Count is disabled, the same number of samples will be used as defined in Stochastic Sampling.