For a description of generic settings common to all tools in the Toolbox, see Working in Tool Settings Dialog Boxes.
Columns are made up of two components: a core, and an optional veneer.
For more information, see Columns.
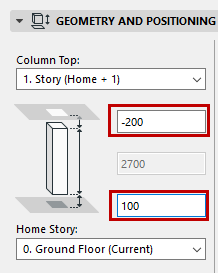
Column Geometry and Positioning Panel
By default:
•The Column top is linked to one story up
•The Home Story is the current story.
For more information, see Home Story.
Use the controls in this panel to change any of these values, and to define the geometry of the Column element.
The Column bottom is always linked to the Home Story, but you can offset the bottom in either direction.
Column top: Use this control to either top link the Column relative to its Home Story (Home+1, Home+2, etc.), or to make it a fixed-height Column (choose “Not linked”).
If you later modify the positions and heights of stories in your projects, the heights of any linked Columns will follow automatically.
•Optionally, define an offset for the Column top from its top linked story. (For a top linked Column, the Column height changes accordingly.) This offset value can be positive, negative or zero.
The offset field is not available if the Column has no top link.

Column height: Enter a value for the total height of the Column. (For a top linked Column, this field is not editable.)
•The Column height value is affected by the top and bottom offsets, if any. If you change the top offset of a top linked Column, or its bottom offset from the Home Story, this change will be reflected in the height value.
Home Story
Choose one of the following Home Story settings:
•The current story: The Column’s Home Story will be the current story, on which it is placed.
•Choose a story to which to link the bottom of the Column. Click Select Story to bring up the full list of stories in the project, if they are not all shown in the list.
•Optionally, define an offset for the Column bottom from its Home Story (the Column height changes accordingly).
The bottom of the Column is physically linked to its Home Story. If you later modify this story’s position (e.g. redefine the floor level), the Column will change its position (while respecting the defined offset, if any).
If you delete the Column’s Home Story, the Column will be deleted, along with all other elements located on the story.
If you change a Column’s elevation so that its bottom is moved to a different story, you have the option to make the Home Story change to match the element’s new location.
See Change Home Story by Elevation.
For more information, see Home Story.
Bottom Elevation [to Reference level]: Calculates the elevation of the Column’s reference line, as measured from the Reference level (by default, this Reference level is Project Zero). Click the pop-up arrow to change the Reference level, if needed.
Note: Reference levels are defined at Options > Project Preferences > Reference Levels.
For general information on levels, see Reference Levels Preferences.
Note: The Bottom Elevation shows the current elevation of the Column bottom. Thus, this value serves as a calculation tool only, not a link. If you change the position of a Reference level, the Column will not change its position.
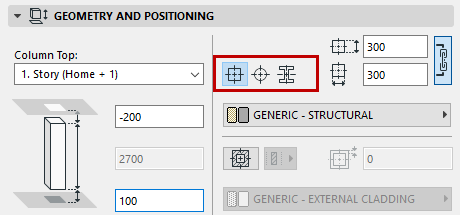
Column Geometry Method, Structure and Dimensions
Click one of three Geometry Method icons to define the cross-section of the column:
•Rectangular
•Circular
•Complex Profile
For a Rectangular or Circular Column:
•Use the pop-up to choose its Building Material.
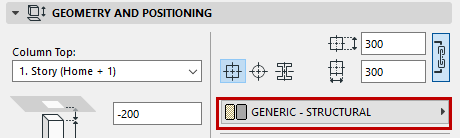
•Enter values for the core dimension(s) in the fields to the right. (For a rectangular, enter horizontal and vertical values. For a circular column, enter a diameter.)
Note: The horizontal and vertical dimensions of Columns with a rectangular cross-section can differ. Use the chain icon next to them to constrain them to the same value.
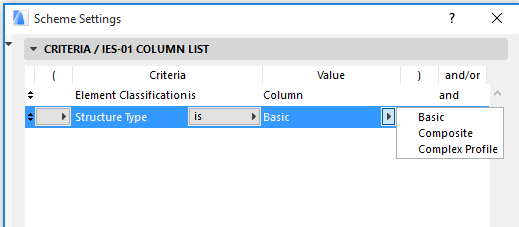
Note: When listing columns by the Structure Type criteria in the Interactive Schedule, “Basic” value will list columns having either a rectangular or circular cross-section.
For a Complex column:
•Use the pop-up to choose its Profile.
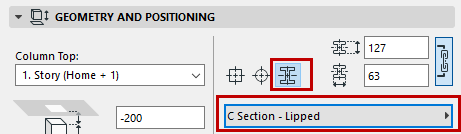
Note: This pop-up shows only those Profiles whose “Use With” control includes Columns. Profiles are defined at Options > Element Attributes > Profile Manager.
•Enter the Column’s horizontal and vertical dimensions.
Note: The horizontal and vertical dimensions of Columns with a rectangular cross-section can differ. Use the chain icon next to them to constrain them to the same value.
For more information on creating a complex (profile) column, see Place Element or Library Part using a Complex Profile.
See also Use Standard Steel Column or Beam Profile.
Veneer Geometry Method, Structure and Dimensions
Not available for Profile (Complex) Columns.
Add/Remove Veneer: Enable this option if you want the column to include a veneer.
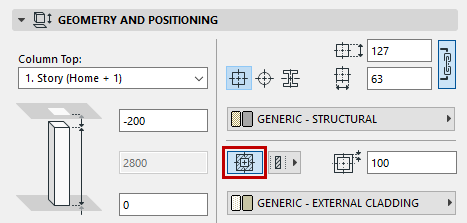
If you have enabled the veneer, enter a value in the field to the right to define the veneer thickness. This thickness is uniform all around the core.
Veneer Structure: By default, the veneer is considered part of the “core” of the column for display and listing purposes.
However, you have the option of defining the column veneer as either “core”, “finish” or “other”. Partial Structure Display settings will take this component definition into account. Choose one of these to define the veneer component:
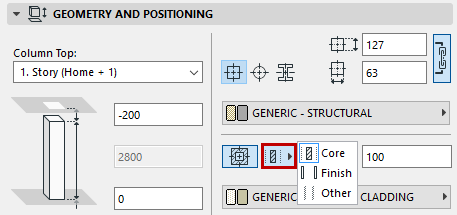
See also Partial Structure Display and Core and Veneer.
The Finish option is not available for wrapped columns. (See Wrapping Method, below.)
Building Material: Use the pop-up to choose a building material for the veneer.
Vertical or Slanted: Click one of these two icons to create either a vertical or a slanted column.
•If you choose the slanted column, enter the slant value in degrees into the Slant angle field to the right.
Note: A column cannot be horizontal; you must enter a number between 1 and 90 degrees.
Rotate Profile: Optionally, enter a rotation angle that will rotate the Column profile.
See also Rotating Beam and Column Profiles.
Wrapping Method: Not available for Profile (Complex) Columns. Click one of two icons to define the column wrapping method for a column that intersects a composite wall: either freestanding or wrapped by walls.
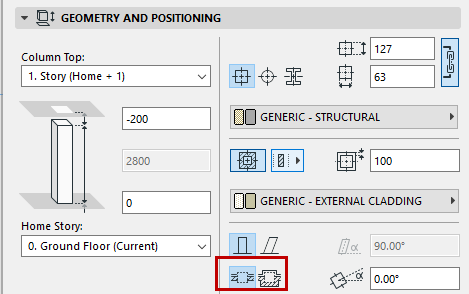
Note: A column whose veneer is defined as “Finish” cannot be wrapped.
See also Columns and Composite Walls.
Anchor Point of Core: Click one of the nine positioning buttons to define the point on the column which will be positioned with the cursor when you click to place the column.
Note: Not available for complex profiles, whose anchor point is the profile origin.
Column Floor Plan and Section Panel
Floor Plan Display
Show on Stories: Choose an option to define which stories will display the column.
•All Relevant Stories: A multi-story column will be displayed and editable on all stories which it intersects. Multi-story columns will be correctly joined with other elements on all stories where the multi-story column is present.
•Home Story Only: This column will be displayed only on its Home Story.
Floor Plan Display: Choose an option to define the Column’s display on the Floor Plan.
•Projected: shows cut part of element’s 3D model, plus its uncut (downward) part.
•Projected with Overhead: shows cut part of element’s 3D model (i.e., as cut at the level of the Floor Plan Cut Plane), plus the element’s overhead part (i.e. the part of the element that is above the Floor Plan Cut Plane.
•Cut Only: displays only the cut part, as cut with the Floor Plan Cut Plane.
Three additional abstract display options are available:
•Symbolic Cut: Available only for vertical columns. The whole floor plan projection of a vertical column (either simple or complex) will be displayed as cut, using its cut line and Building Material attributes, regardless of the column’s vertical position. This option is available only if the Show on Stories control is set to “Home Story only”. The Floor Plan Cut Plane settings do not affect the display of such a column.
•Outlines Only: the entire element’s outline is shown using its uncut attributes.
•Overhead All: the entire element’s outline is shown using its overhead attributes.
The Show Projection pop-up contains three options. (These are available only when the Floor Plan Display option is set to one of the “Projected” options.)
•to Floor Plan Range: Choose to show the element on a range of stories (the current story, plus a given number of stories above and below it.)
If you choose this option, then you can set the desired range (i.e. the number of stories on which to show this element in either direction) in Floor Plan Cut Plane Settings.
•to Absolute Display Limit: Set a fixed lower limit (by default, this is Project Zero), then show all parts of the element above this limit.
If you choose this option, then go to Floor Plan Cut Plane Settings to set the Absolute Display Limit for this element.
•Entire Element: The element will be displayed on all relevant stories.
Note: “Entire element” is the only available projection option for simple straight columns which are set to “Symbolic Cut” in their Floor Plan display. Floor Plan Cut Plane settings do not affect the display of these columns.
For more information, see Floor Plan Cut Plane Settings Dialog Box.
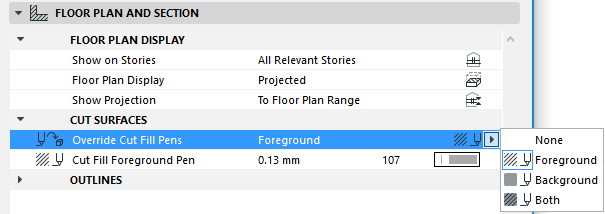
Cut Surfaces: In this section, set the attributes displayed for cut surfaces of the core and veneer (if any), both in Section and on the Floor Plan.
•Define the cut line type and pen for the core and the veneer (if any).
•If needed, override the fill foreground/background pens of this element (defined by default in the Building Material). To do this, choose Foreground, Background or Both from the Override Cut Fill Pens pop-up to access the respective controls.
Outlines: Use these settings to define line types and pen colors to element outlines that fall above (Overhead) and/or below (Uncut) the Floor Plan Cut Plane.
•Overhead Lines will be displayed if the Floor Plan Display pop-up is set to “Projected with Overhead” or “Overhead All”.
•Uncut Lines will be displayed if the Floor Plan Display pop-up is set to “Projected” or “Outlines Only.”
For more information, see Floor Plan Cut Plane (Global Setting) and Define Range of Element’s Projected Display (Show Projection).
Floor Plan Symbol: Use the controls in this section to define settings for the column’s Floor Plan (Crossing) symbol.
•Symbol Type: Choose this parameter, then activate its arrow pop-up to choose one of four crossing symbols: Plain (no cross), Slash, X, and Crosshair.
Note: For a profiled column, only the Plain and crosshair symbols are available. The crosshair symbolizes the column’s axis and will revolve along with the column cross section.
•Enter a Column Cross Line Pen color.
•If you have chosen Crosshair, you have two additional settings:
Distance From Center: Enter the distance of each crosshair line from the column’s centerpoint.
Length Outside Column: Enter the length by which the crosshair line should extend past the edge of the column.
Although the crosshair is a graphic symbol and not part of the model, the crosshair will be resized (together with the column itself) if you change the drawing’s scale.
To show or hide the crossing symbol of columns on the Floor Plan, check/uncheck the “Show Column Symbol” box in Document > Model View > Model View Options > Options for Construction Elements.
Override Surface: Use this pop-up if you wish to override the surface assigned to this element (in its Building Material).
Note: For Columns placed with the Wrapped method, the choice you make here is overridden by the surfaces of the Walls that they intersect.
Note: For a Profile Column, you can also apply a Custom surface to any edge(s) of the profile element.
Custom Texture Alignment: If this message is activated, it indicates that the currently selected column (already placed in the project) has been assigned a custom 3D texture.
•In this case, the Reset Texture button is also activated. Click to restore the origin of the Texture of the selected column.
For more information, see Align 3D Texture.
Relation to Zones: Click this pop-up field to define the relationship of the Column to Zones. The list defines whether the new Column is a Zone delimiter, an element to subtract from the Zone’s area or to be ignored when calculating Zones.
•Zone Boundary (not available for slanted columns): This option means that a vertical column located inside a zone will not be included when the zone area or zone volume is calculated. The zone boundary is drawn at the base of the column. Multi-story elements in automatic display mode can serve as zone boundaries on any story on which they exist, not just their Home Story.
•Reduce Zone Area Only means that the2D zone will encompass the column, but the column area will not be included in the zone area. (Zone Volume, however, will include the column.)
•Subtract from Zones means that when calculating the zone’s 3D volume, the volume will not include the volume of any column located inside the zone. The 2D Zone will not include the Column area either.
•No Effect On Zones means that the column has no effect on the zone; the zone area and volume will include the area covered by the column.
Related Topics: